
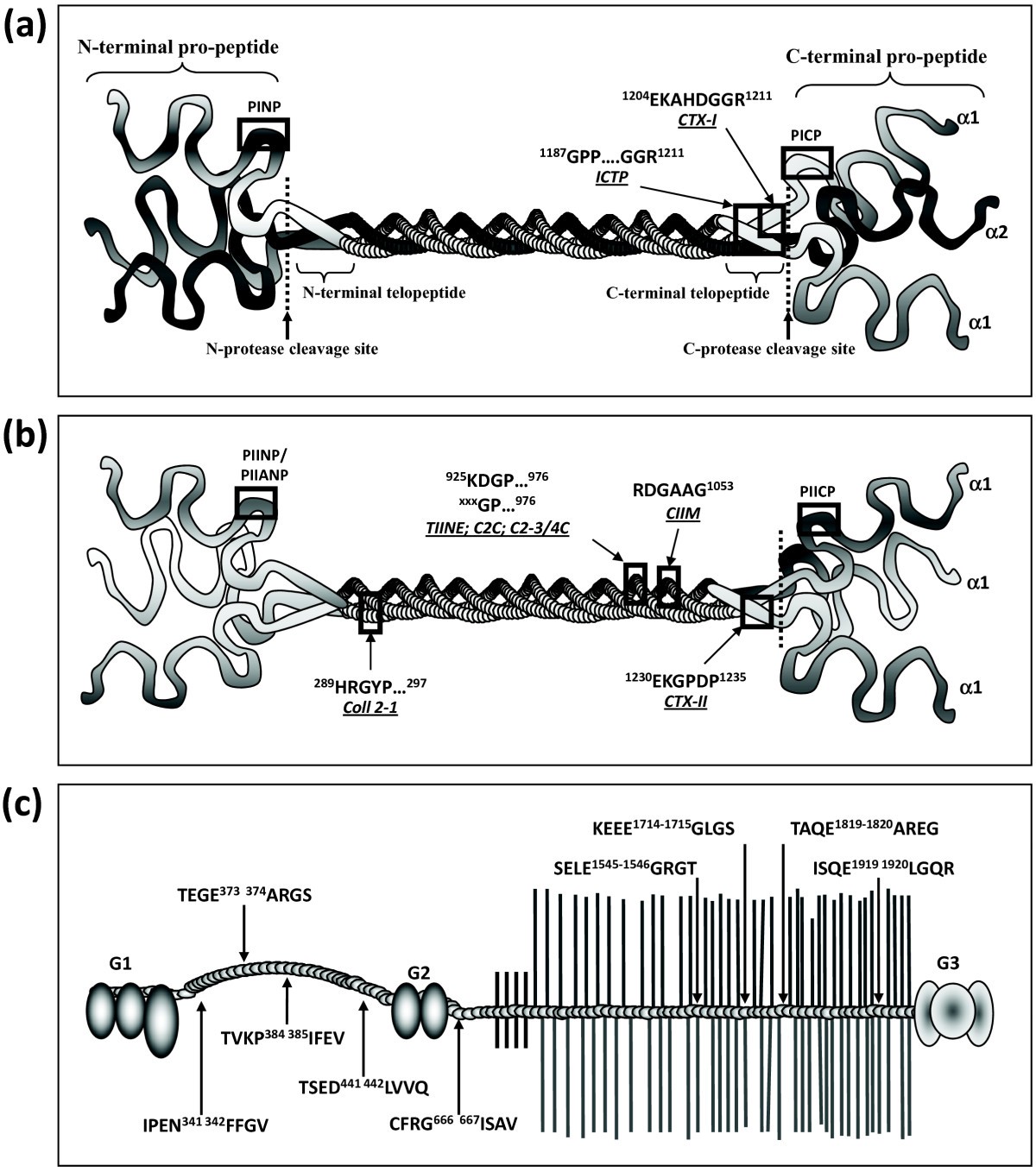
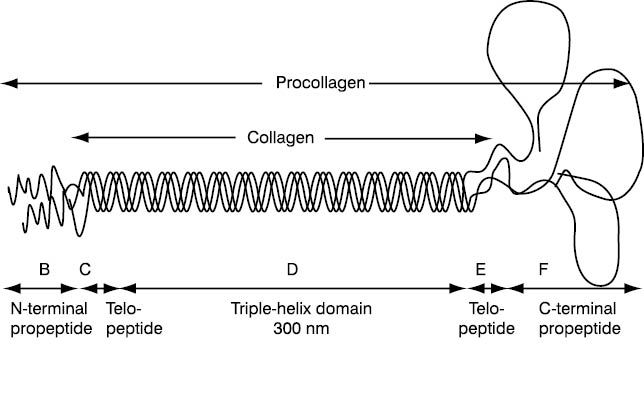
The amino- and carboxyterminal cross-linked telopeptides of collagen type I, NTX-I and CTX-I: A comparative review - ScienceDirect
Review Serological assessment of type I collagen burden in scleroderma spectrum disorders: A systematic review
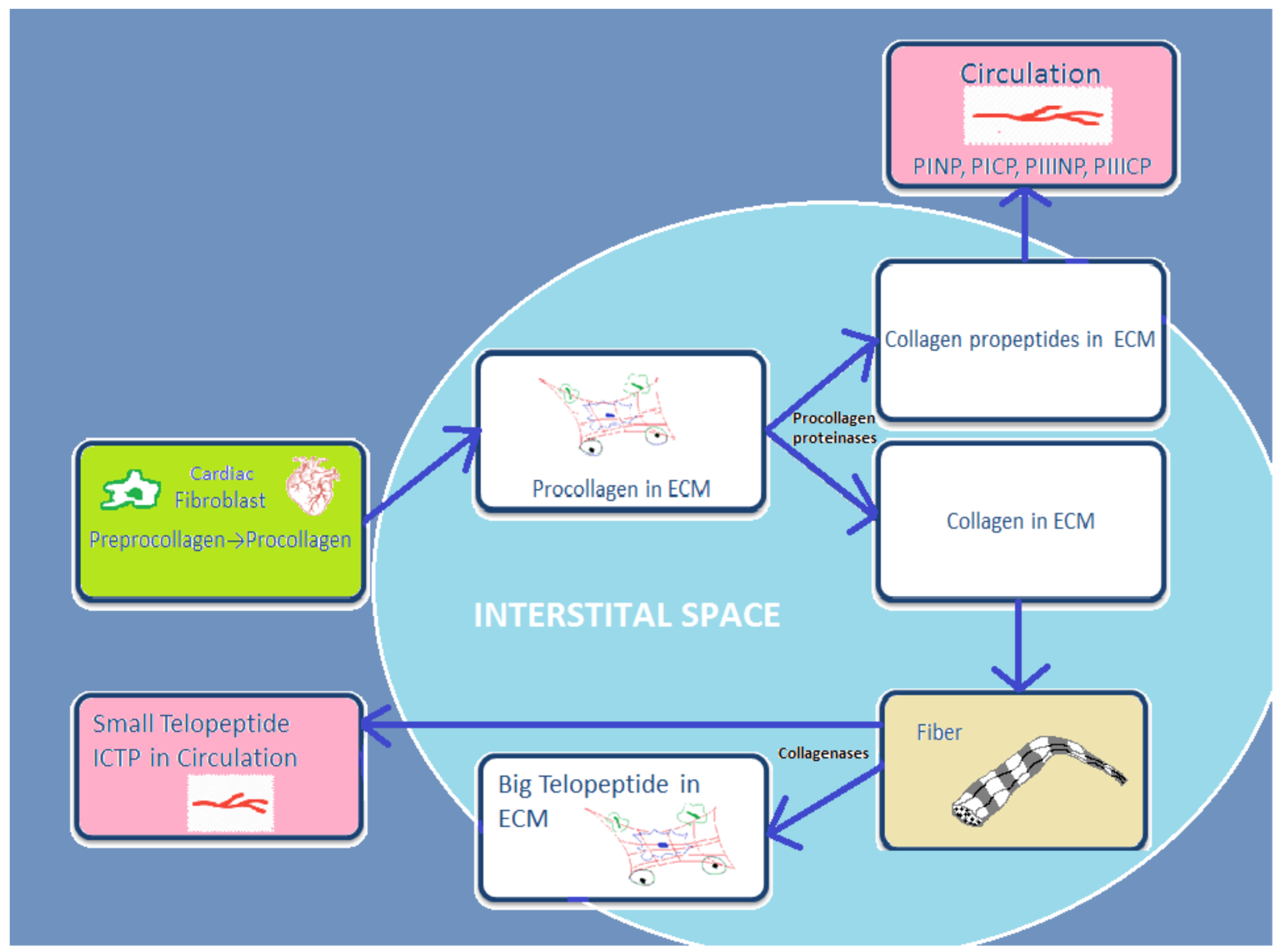
Metabolites | Free Full-Text | Extracellular Matrix in Heart Disease: Focus on Circulating Collagen Type I and III Derived Peptides as Biomarkers of Myocardial Fibrosis and Their Potential in the Prognosis of

Procollagen Type 1 N Terminal Propeptide P1np (Immunodiagnostic Systems) | Bioz | Ratings For Life-Science Research

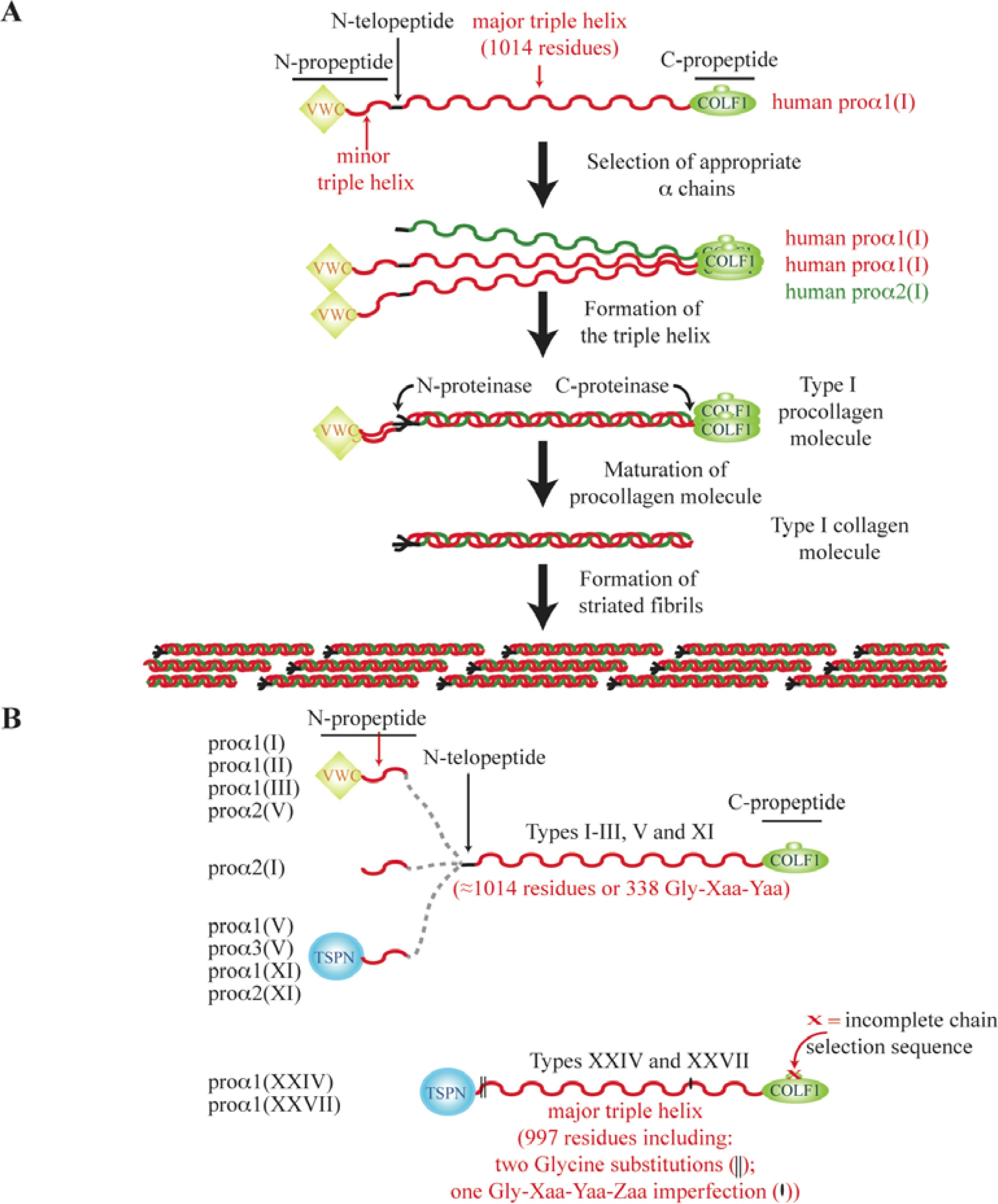
Bone Morphogenetic Protein-1 Processes the NH2-terminal Propeptide, and a Furin-like Proprotein Convertase Processes the COOH-terminal Propeptide of pro-α1(V) Collagen* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
-ELISA-NBP2-76466-img0002.jpg)
Mouse Procollagen Type 1 N-Terminal Propeptide ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) (NBP2-76466): Novus Biologicals
Metalloproteases meprin α and meprin β are C- and N-procollagen proteinases important for collagen assembly and tensile st
-NBP2-81204-img0001.jpg)
Mouse Procollagen type III N-terminal Propeptide ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) (NBP2-81204): Novus Biologicals

The NH2-terminal Propeptide of Type I Procollagen Acts Intracellularly to Modulate Cell Function* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Severely restricting energy intake for 24 h does not affect markers of bone metabolism at rest or in response to re-feeding | SpringerLink

Sequence-dependent mechanics of collagen reflect its structural and functional organization | bioRxiv

Endoplasmic Reticulum-mediated Quality Control of Type I Collagen Production by Cells from Osteogenesis Imperfecta Patients with Mutations in the proα1(I) Chain Carboxyl-terminal Propeptide which Impair Subunit Assembly * - Journal of Biological
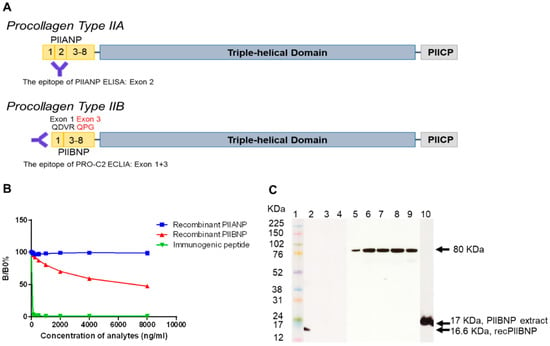
IJMS | Free Full-Text | A Novel High Sensitivity Type II Collagen Blood-Based Biomarker, PRO-C2, for Assessment of Cartilage Formation | HTML
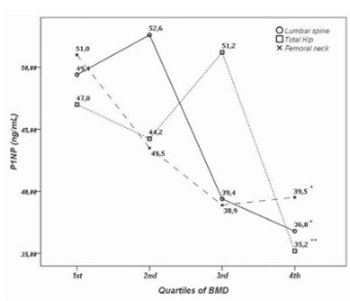
The utility of procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide for the bone status assessment in postmenopausal women | Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
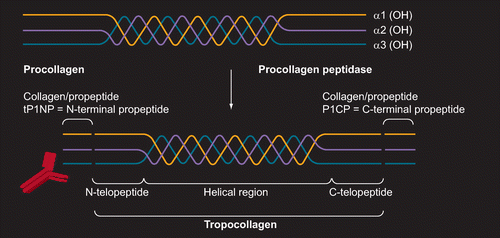
Role of serum P1NP measurement for monitoring treatment response in osteoporosis | Biomarkers in Medicine






![Anti-Collagen Alpha-1(I) Chain Carboxy-Propeptide [LF-42] Antibody - Kerafast Anti-Collagen Alpha-1(I) Chain Carboxy-Propeptide [LF-42] Antibody - Kerafast](https://www.kerafast.com/MediaStorage/Product/Images/Large/1383_2001202001264513820.jpg)